10. 图像的几何变换#
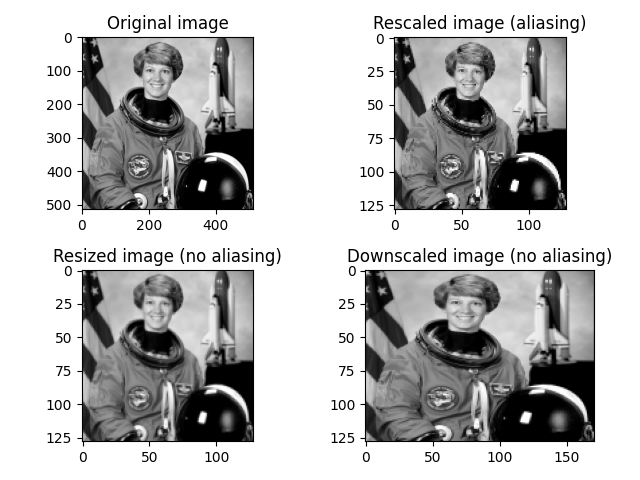
10.1. 裁剪、调整大小和重新缩放图像#
图像是 NumPy 数组(如图像的 NumPy 速成课程章节所述),裁剪图像可以使用简单的切片操作来完成。下面我们裁剪一个对应于宇航员图像左上角的 100x100 正方形。请注意,此操作是针对所有颜色通道完成的(颜色维度是最后一个,即第三个维度)。
>>> import skimage as ski
>>> img = ski.data.astronaut()
>>> top_left = img[:100, :100]
为了改变图像的形状,skimage.color 提供了重新缩放、调整大小和缩小中描述的几个函数。
from skimage import data, color
from skimage.transform import rescale, resize, downscale_local_mean
image = color.rgb2gray(data.astronaut())
image_rescaled = rescale(image, 0.25, anti_aliasing=False)
image_resized = resize(
image, (image.shape[0] // 4, image.shape[1] // 4), anti_aliasing=True
)
image_downscaled = downscale_local_mean(image, (4, 3))

10.2. 投影变换(单应性)#
单应性是保持点对齐的欧几里得空间的变换。单应性的具体情况对应于更多属性的守恒,例如平行性(仿射变换)、形状(相似变换)或距离(欧几里得变换)。scikit-image 中可用的不同类型的单应性在单应性的类型中进行了介绍。
投影变换可以使用显式参数(例如,缩放、剪切、旋转和平移)来创建
import numpy as np
import skimage as ski
tform = ski.transform.EuclideanTransform(
rotation=np.pi / 12.,
translation = (100, -20)
)
或完整的变换矩阵
matrix = np.array([[np.cos(np.pi/12), -np.sin(np.pi/12), 100],
[np.sin(np.pi/12), np.cos(np.pi/12), -20],
[0, 0, 1]])
tform = ski.transform.EuclideanTransform(matrix)
变换的变换矩阵可作为其tform.params属性使用。可以通过使用@矩阵乘法运算符来乘以矩阵来组成变换。
变换矩阵使用齐次坐标,这是欧几里得几何中使用的笛卡尔坐标的扩展,用于更一般的投影几何。特别是,无穷远的点可以用有限的坐标表示。
可以使用skimage.transform.warp()将变换应用于图像
img = ski.util.img_as_float(ski.data.chelsea())
tf_img = ski.transform.warp(img, tform.inverse)

skimage.transform中的不同变换都有一个estimate方法,以便从两组点(源点和目标点)估计变换的参数,如使用几何变换教程中所述
text = ski.data.text()
src = np.array([[0, 0], [0, 50], [300, 50], [300, 0]])
dst = np.array([[155, 15], [65, 40], [260, 130], [360, 95]])
tform3 = ski.transform.ProjectiveTransform()
tform3.estimate(src, dst)
warped = ski.transform.warp(text, tform3, output_shape=(50, 300))
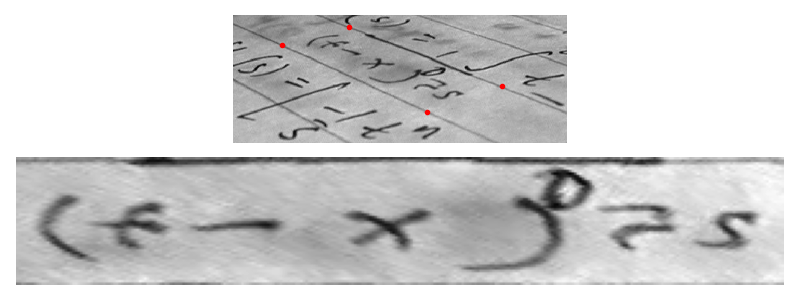
estimate方法使用最小二乘优化来最小化源和优化之间的距离。源点和目标点可以手动确定,或者使用skimage.feature中可用的不同特征检测方法,例如
角点检测,
等等。
以及在使用skimage.feature.match_descriptors()匹配点之后估计变换参数。但是,经常会产生虚假匹配,建议使用 RANSAC 算法(而不是简单的最小二乘优化)来提高对异常值的鲁棒性,如使用 RANSAC 的稳健匹配中所述。
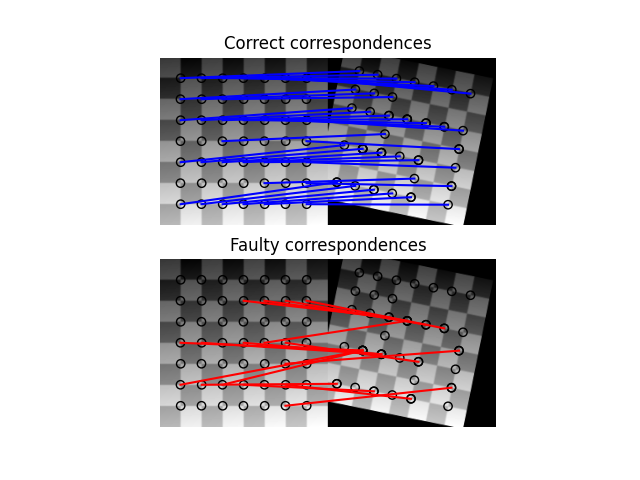
显示变换估计应用的示例有
estimate方法是基于点的,也就是说,它只使用来自源图像和目标图像的一组点。对于估计平移(偏移),也可以使用基于傅里叶空间互相关的使用所有像素的全场方法。此方法由skimage.registration.phase_cross_correlation()实现,并在图像配准教程中进行了解释。

使用极坐标和对数极坐标变换进行配准教程通过首先使用对数极坐标变换,解释了这种用于估计旋转的全场方法的变体。
