注意
转到末尾以下载完整示例代码。或通过 Binder 在浏览器中运行此示例
直方图匹配#
此示例演示了直方图匹配的功能。它操作输入图像的像素,使其直方图与参考图像的直方图匹配。如果图像有多个通道,只要输入图像和参考图像中的通道数相等,则为每个通道独立完成匹配。
直方图匹配可以用作图像处理的轻量级归一化,例如特征匹配,特别是在图像来自不同来源或在不同条件(即照明)下拍摄的情况下。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage import data
from skimage import exposure
from skimage.exposure import match_histograms
reference = data.coffee()
image = data.chelsea()
matched = match_histograms(image, reference, channel_axis=-1)
fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(
nrows=1, ncols=3, figsize=(8, 3), sharex=True, sharey=True
)
for aa in (ax1, ax2, ax3):
aa.set_axis_off()
ax1.imshow(image)
ax1.set_title('Source')
ax2.imshow(reference)
ax2.set_title('Reference')
ax3.imshow(matched)
ax3.set_title('Matched')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()

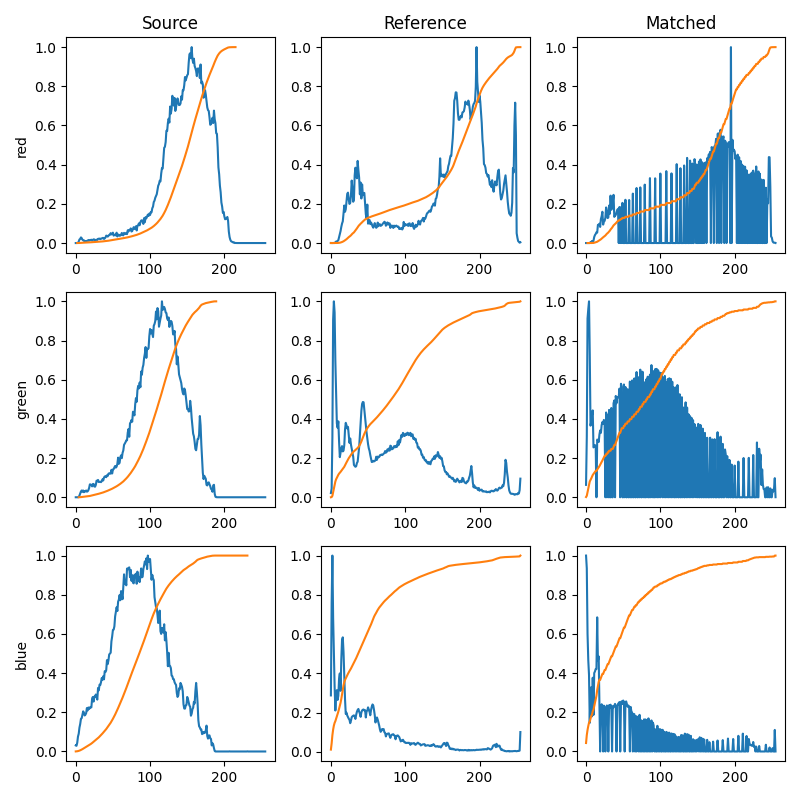
为了说明直方图匹配的效果,我们针对每个 RGB 通道绘制直方图和累积直方图。 显然,匹配图像对于每个通道都具有与参考图像相同的累积直方图。
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=3, ncols=3, figsize=(8, 8))
for i, img in enumerate((image, reference, matched)):
for c, c_color in enumerate(('red', 'green', 'blue')):
img_hist, bins = exposure.histogram(img[..., c], source_range='dtype')
axes[c, i].plot(bins, img_hist / img_hist.max())
img_cdf, bins = exposure.cumulative_distribution(img[..., c])
axes[c, i].plot(bins, img_cdf)
axes[c, 0].set_ylabel(c_color)
axes[0, 0].set_title('Source')
axes[0, 1].set_title('Reference')
axes[0, 2].set_title('Matched')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
脚本的总运行时间:(0 分 1.684 秒)
