注意
转到末尾下载完整的示例代码。或通过 Binder 在浏览器中运行此示例
评估分割指标#
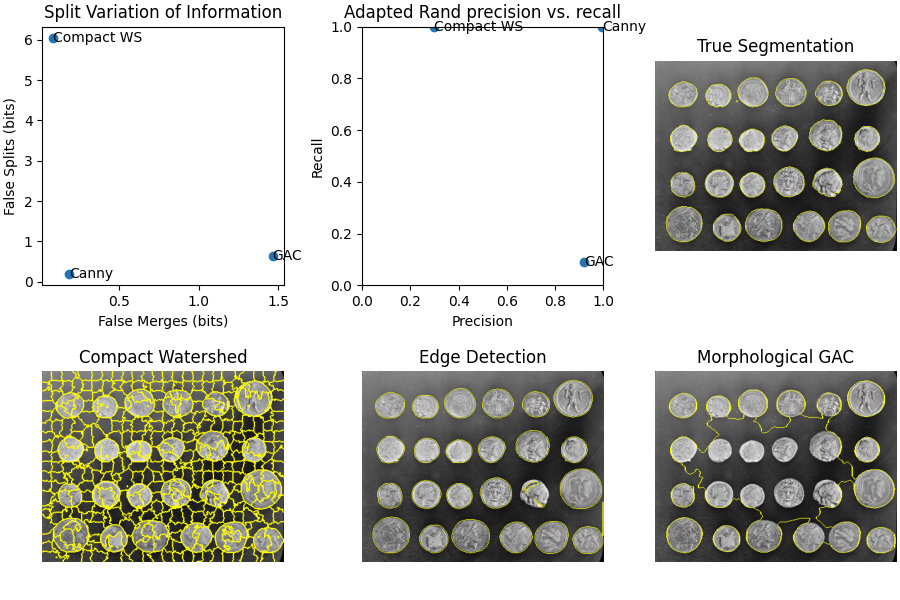
在尝试不同的分割方法时,如何知道哪种方法最好?如果您有真实值或金标准分割,您可以使用各种指标来检查每种自动化方法与真实值有多接近。在此示例中,我们使用一个易于分割的图像作为示例,说明如何解释各种分割指标。我们将使用调整后的 Rand 误差和信息变异作为示例指标,并查看过度分割(将真实分割拆分为太多子分割)和欠分割(将不同的真实分割合并为一个分割)如何影响不同的分数。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import ndimage as ndi
from skimage import data
from skimage.metrics import adapted_rand_error, variation_of_information
from skimage.filters import sobel
from skimage.measure import label
from skimage.util import img_as_float
from skimage.feature import canny
from skimage.morphology import remove_small_objects
from skimage.segmentation import (
morphological_geodesic_active_contour,
inverse_gaussian_gradient,
watershed,
mark_boundaries,
)
image = data.coins()
首先,我们生成真实的分割。对于这个简单的图像,我们知道能够产生完美分割的精确函数和参数。在实际场景中,通常您会通过手动注释或分割的“绘制”来生成真实值。
elevation_map = sobel(image)
markers = np.zeros_like(image)
markers[image < 30] = 1
markers[image > 150] = 2
im_true = watershed(elevation_map, markers)
im_true = ndi.label(ndi.binary_fill_holes(im_true - 1))[0]
接下来,我们创建三个具有不同特征的不同分割。第一个使用skimage.segmentation.watershed(),其中紧凑性是一个有用的初始分割,但作为最终结果太精细。我们将看到这如何导致过度分割指标飙升。
下一个方法使用 Canny 边缘滤波器,skimage.feature.canny()。这是一个非常好的边缘查找器,并且给出了平衡的结果。
edges = canny(image)
fill_coins = ndi.binary_fill_holes(edges)
im_test2 = ndi.label(remove_small_objects(fill_coins, 21))[0]
最后,我们使用形态学测地线主动轮廓,skimage.segmentation.morphological_geodesic_active_contour(),该方法通常会产生良好的结果,但需要很长时间才能收敛到好的答案。我们特意在 100 次迭代时缩短了该过程,以便最终结果是欠分割,这意味着许多区域合并为一个分割。我们将看到分割指标上的相应影响。
image = img_as_float(image)
gradient = inverse_gaussian_gradient(image)
init_ls = np.zeros(image.shape, dtype=np.int8)
init_ls[10:-10, 10:-10] = 1
im_test3 = morphological_geodesic_active_contour(
gradient,
num_iter=100,
init_level_set=init_ls,
smoothing=1,
balloon=-1,
threshold=0.69,
)
im_test3 = label(im_test3)
method_names = [
'Compact watershed',
'Canny filter',
'Morphological Geodesic Active Contours',
]
short_method_names = ['Compact WS', 'Canny', 'GAC']
precision_list = []
recall_list = []
split_list = []
merge_list = []
for name, im_test in zip(method_names, [im_test1, im_test2, im_test3]):
error, precision, recall = adapted_rand_error(im_true, im_test)
splits, merges = variation_of_information(im_true, im_test)
split_list.append(splits)
merge_list.append(merges)
precision_list.append(precision)
recall_list.append(recall)
print(f'\n## Method: {name}')
print(f'Adapted Rand error: {error}')
print(f'Adapted Rand precision: {precision}')
print(f'Adapted Rand recall: {recall}')
print(f'False Splits: {splits}')
print(f'False Merges: {merges}')
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 3, figsize=(9, 6), constrained_layout=True)
ax = axes.ravel()
ax[0].scatter(merge_list, split_list)
for i, txt in enumerate(short_method_names):
ax[0].annotate(txt, (merge_list[i], split_list[i]), verticalalignment='center')
ax[0].set_xlabel('False Merges (bits)')
ax[0].set_ylabel('False Splits (bits)')
ax[0].set_title('Split Variation of Information')
ax[1].scatter(precision_list, recall_list)
for i, txt in enumerate(short_method_names):
ax[1].annotate(txt, (precision_list[i], recall_list[i]), verticalalignment='center')
ax[1].set_xlabel('Precision')
ax[1].set_ylabel('Recall')
ax[1].set_title('Adapted Rand precision vs. recall')
ax[1].set_xlim(0, 1)
ax[1].set_ylim(0, 1)
ax[2].imshow(mark_boundaries(image, im_true))
ax[2].set_title('True Segmentation')
ax[2].set_axis_off()
ax[3].imshow(mark_boundaries(image, im_test1))
ax[3].set_title('Compact Watershed')
ax[3].set_axis_off()
ax[4].imshow(mark_boundaries(image, im_test2))
ax[4].set_title('Edge Detection')
ax[4].set_axis_off()
ax[5].imshow(mark_boundaries(image, im_test3))
ax[5].set_title('Morphological GAC')
ax[5].set_axis_off()
plt.show()
## Method: Compact watershed
Adapted Rand error: 0.6696040824674964
Adapted Rand precision: 0.19789866776616444
Adapted Rand recall: 0.999747618854942
False Splits: 6.235700763571577
False Merges: 0.10855347108404328
## Method: Canny filter
Adapted Rand error: 0.01477976422795424
Adapted Rand precision: 0.9829789913922441
Adapted Rand recall: 0.9874717238207291
False Splits: 0.11790842956314956
False Merges: 0.17056628682718059
## Method: Morphological Geodesic Active Contours
Adapted Rand error: 0.8380351755097508
Adapted Rand precision: 0.8878701134692834
Adapted Rand recall: 0.08911012454398565
False Splits: 0.6563768831046463
False Merges: 1.5482985465714199
脚本总运行时间:(0 分钟 3.510 秒)
