注意
转到末尾下载完整示例代码。或通过 Binder 在浏览器中运行此示例
区域邻接图(RAG)合并#
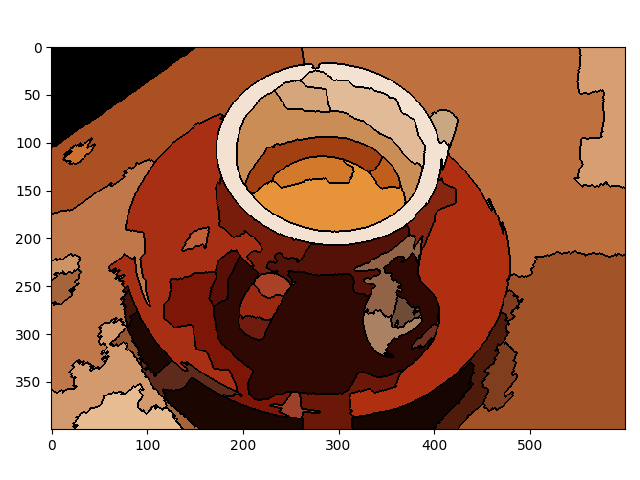
此示例构建一个区域邻接图 (RAG),并逐步合并颜色相似的区域。合并两个相邻区域会生成一个包含合并区域中所有像素的新区域。区域会一直合并,直到不再有高度相似的区域对。
from skimage import data, segmentation, color
from skimage import graph
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def _weight_mean_color(graph, src, dst, n):
"""Callback to handle merging nodes by recomputing mean color.
The method expects that the mean color of `dst` is already computed.
Parameters
----------
graph : RAG
The graph under consideration.
src, dst : int
The vertices in `graph` to be merged.
n : int
A neighbor of `src` or `dst` or both.
Returns
-------
data : dict
A dictionary with the `"weight"` attribute set as the absolute
difference of the mean color between node `dst` and `n`.
"""
diff = graph.nodes[dst]['mean color'] - graph.nodes[n]['mean color']
diff = np.linalg.norm(diff)
return {'weight': diff}
def merge_mean_color(graph, src, dst):
"""Callback called before merging two nodes of a mean color distance graph.
This method computes the mean color of `dst`.
Parameters
----------
graph : RAG
The graph under consideration.
src, dst : int
The vertices in `graph` to be merged.
"""
graph.nodes[dst]['total color'] += graph.nodes[src]['total color']
graph.nodes[dst]['pixel count'] += graph.nodes[src]['pixel count']
graph.nodes[dst]['mean color'] = (
graph.nodes[dst]['total color'] / graph.nodes[dst]['pixel count']
)
img = data.coffee()
labels = segmentation.slic(img, compactness=30, n_segments=400, start_label=1)
g = graph.rag_mean_color(img, labels)
labels2 = graph.merge_hierarchical(
labels,
g,
thresh=35,
rag_copy=False,
in_place_merge=True,
merge_func=merge_mean_color,
weight_func=_weight_mean_color,
)
out = color.label2rgb(labels2, img, kind='avg', bg_label=0)
out = segmentation.mark_boundaries(out, labels2, (0, 0, 0))
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.imshow(out)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
脚本的总运行时间:(0 分 4.305 秒)
