注意
转到结尾 下载完整的示例代码。或通过 Binder 在浏览器中运行此示例
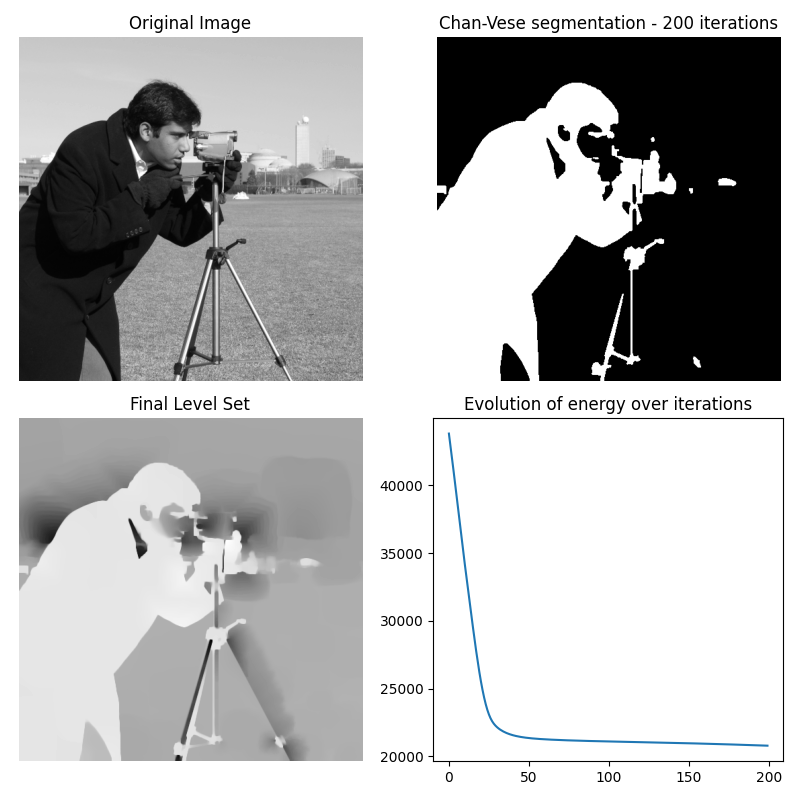
Chan-Vese 分割#
Chan-Vese 分割算法旨在分割边界不清晰的对象。该算法基于水平集,通过迭代演化来最小化能量,该能量由对应于分割区域外部的平均值与强度差异之和的加权值、分割区域内部的平均值与差异之和以及取决于分割区域边界长度的项定义。
该算法最初由 Tony Chan 和 Luminita Vese 在一篇题为“无边缘的主动轮廓模型”的出版物中提出[1]。另请参阅[2],[3]。
该算法的实现有些简化,因为原始论文中描述的面积因子“nu”未实现,并且仅适用于灰度图像。
lambda1 和 lambda2 的典型值是 1。如果“背景”在分布方面与分割对象非常不同(例如,具有不同强度数字的均匀黑色图像),则这些值应彼此不同。
mu 的典型值介于 0 和 1 之间,但在处理轮廓非常不明确的形状时可以使用更高的值。
该算法还会返回一个值列表,该列表对应于每次迭代的能量。这可用于调整上述各种参数。
参考文献#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage import data, img_as_float
from skimage.segmentation import chan_vese
image = img_as_float(data.camera())
# Feel free to play around with the parameters to see how they impact the result
cv = chan_vese(
image,
mu=0.25,
lambda1=1,
lambda2=1,
tol=1e-3,
max_num_iter=200,
dt=0.5,
init_level_set="checkerboard",
extended_output=True,
)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(8, 8))
ax = axes.flatten()
ax[0].imshow(image, cmap="gray")
ax[0].set_axis_off()
ax[0].set_title("Original Image", fontsize=12)
ax[1].imshow(cv[0], cmap="gray")
ax[1].set_axis_off()
title = f'Chan-Vese segmentation - {len(cv[2])} iterations'
ax[1].set_title(title, fontsize=12)
ax[2].imshow(cv[1], cmap="gray")
ax[2].set_axis_off()
ax[2].set_title("Final Level Set", fontsize=12)
ax[3].plot(cv[2])
ax[3].set_title("Evolution of energy over iterations", fontsize=12)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
脚本的总运行时间:(0 分钟 4.440 秒)
