注意
转到末尾以下载完整的示例代码。或者通过 Binder 在您的浏览器中运行此示例
滑动窗口直方图#
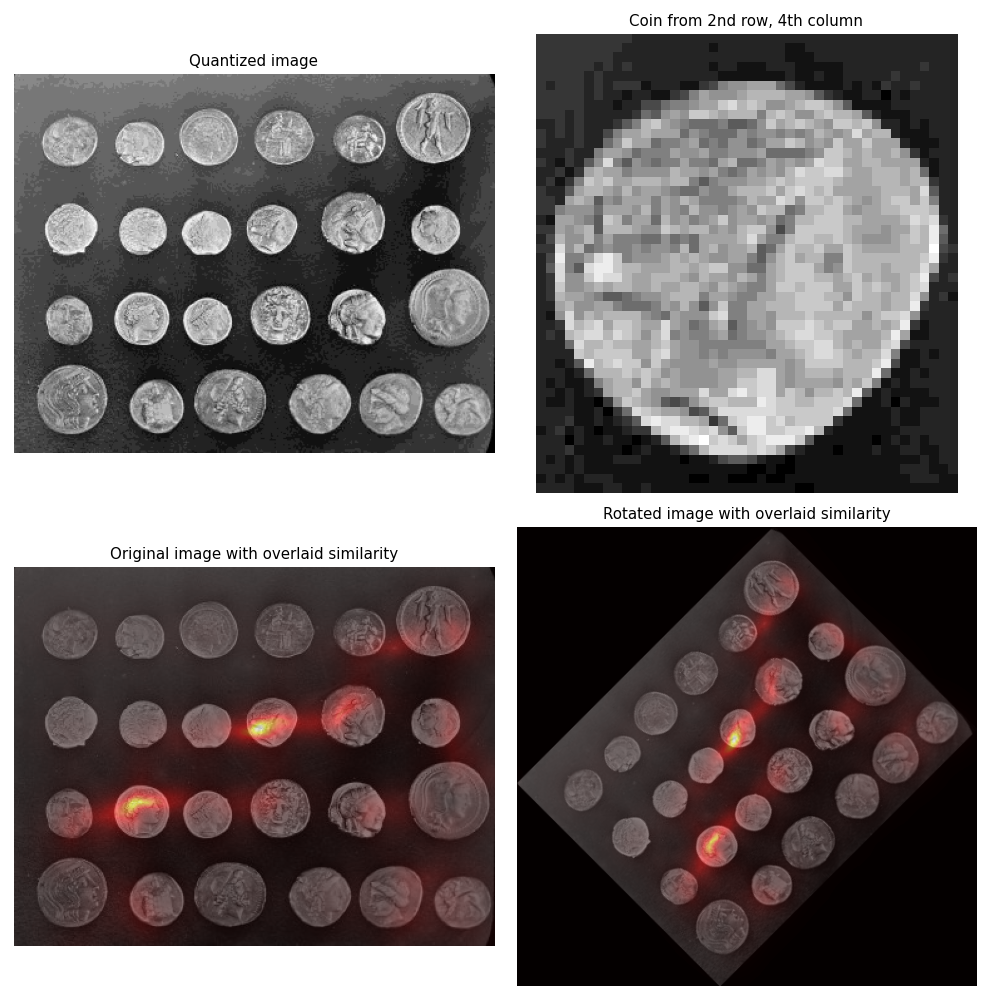
直方图匹配可用于图像中的对象检测 [1]。此示例从 skimage.data.coins 图像中提取单个硬币,并使用直方图匹配尝试在原始图像中定位它。
首先,提取包含目标硬币的图像的盒状区域,并计算其灰度值的直方图。
接下来,对于测试图像中的每个像素,计算图像中围绕该像素的区域中的灰度值的直方图。skimage.filters.rank.windowed_histogram 用于此任务,因为它采用高效的基于滑动窗口的算法,能够快速计算这些直方图 [2]。将图像中每个像素周围区域的局部直方图与单个硬币的直方图进行比较,并计算和显示相似性度量。
单个硬币的直方图是使用 numpy.histogram 在围绕硬币的盒状区域上计算的,而滑动窗口直方图是使用略微不同大小的圆盘形结构元素计算的。这样做是为了证明该技术尽管存在这些差异仍然可以找到相似性。
为了演示该技术的旋转不变性,在旋转 45 度的硬币图像版本上执行相同的测试。
参考文献#
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage import data, transform
from skimage.util import img_as_ubyte
from skimage.morphology import disk
from skimage.filters import rank
matplotlib.rcParams['font.size'] = 9
def windowed_histogram_similarity(image, footprint, reference_hist, n_bins):
# Compute normalized windowed histogram feature vector for each pixel
px_histograms = rank.windowed_histogram(image, footprint, n_bins=n_bins)
# Reshape coin histogram to (1,1,N) for broadcast when we want to use it in
# arithmetic operations with the windowed histograms from the image
reference_hist = reference_hist.reshape((1, 1) + reference_hist.shape)
# Compute Chi squared distance metric: sum((X-Y)^2 / (X+Y));
# a measure of distance between histograms
X = px_histograms
Y = reference_hist
num = (X - Y) ** 2
denom = X + Y
denom[denom == 0] = np.inf
frac = num / denom
chi_sqr = 0.5 * np.sum(frac, axis=2)
# Generate a similarity measure. It needs to be low when distance is high
# and high when distance is low; taking the reciprocal will do this.
# Chi squared will always be >= 0, add small value to prevent divide by 0.
similarity = 1 / (chi_sqr + 1.0e-4)
return similarity
# Load the `skimage.data.coins` image
img = img_as_ubyte(data.coins())
# Quantize to 16 levels of grayscale; this way the output image will have a
# 16-dimensional feature vector per pixel
quantized_img = img // 16
# Select the coin from the 4th column, second row.
# Coordinate ordering: [x1,y1,x2,y2]
coin_coords = [184, 100, 228, 148] # 44 x 44 region
coin = quantized_img[coin_coords[1] : coin_coords[3], coin_coords[0] : coin_coords[2]]
# Compute coin histogram and normalize
coin_hist, _ = np.histogram(coin.flatten(), bins=16, range=(0, 16))
coin_hist = coin_hist.astype(float) / np.sum(coin_hist)
# Compute a disk shaped mask that will define the shape of our sliding window
# Example coin is ~44px across, so make a disk 61px wide (2 * rad + 1) to be
# big enough for other coins too.
footprint = disk(30)
# Compute the similarity across the complete image
similarity = windowed_histogram_similarity(
quantized_img, footprint, coin_hist, coin_hist.shape[0]
)
# Now try a rotated image
rotated_img = img_as_ubyte(transform.rotate(img, 45.0, resize=True))
# Quantize to 16 levels as before
quantized_rotated_image = rotated_img // 16
# Similarity on rotated image
rotated_similarity = windowed_histogram_similarity(
quantized_rotated_image, footprint, coin_hist, coin_hist.shape[0]
)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize=(10, 10))
axes[0, 0].imshow(quantized_img, cmap='gray')
axes[0, 0].set_title('Quantized image')
axes[0, 0].axis('off')
axes[0, 1].imshow(coin, cmap='gray')
axes[0, 1].set_title('Coin from 2nd row, 4th column')
axes[0, 1].axis('off')
axes[1, 0].imshow(img, cmap='gray')
axes[1, 0].imshow(similarity, cmap='hot', alpha=0.5)
axes[1, 0].set_title('Original image with overlaid similarity')
axes[1, 0].axis('off')
axes[1, 1].imshow(rotated_img, cmap='gray')
axes[1, 1].imshow(rotated_similarity, cmap='hot', alpha=0.5)
axes[1, 1].set_title('Rotated image with overlaid similarity')
axes[1, 1].axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
脚本总运行时间:(0 分钟 2.292 秒)
